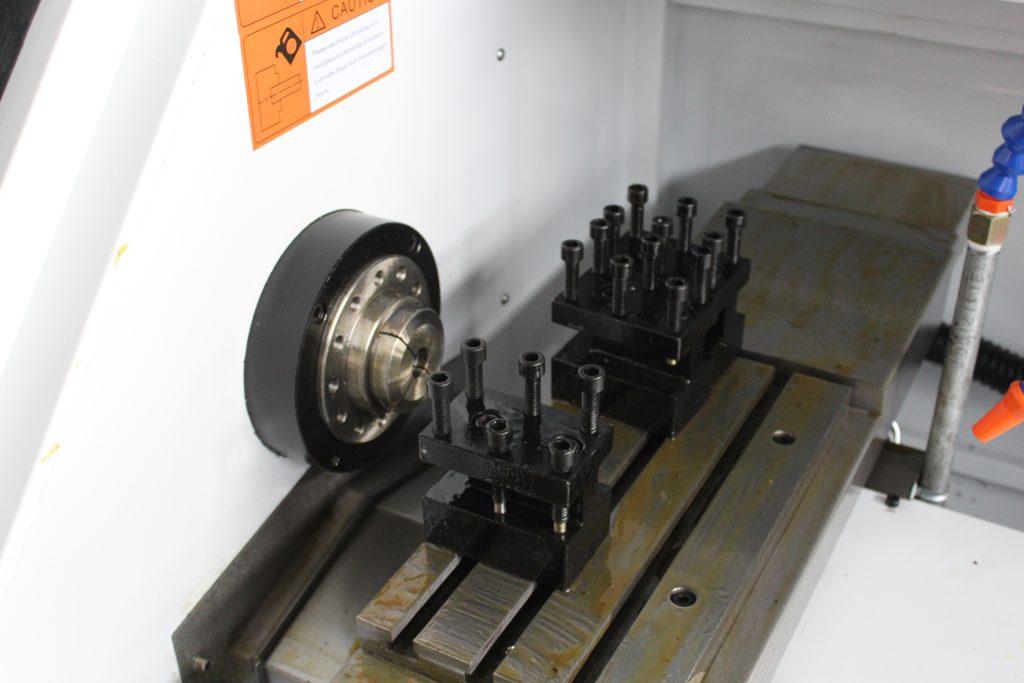
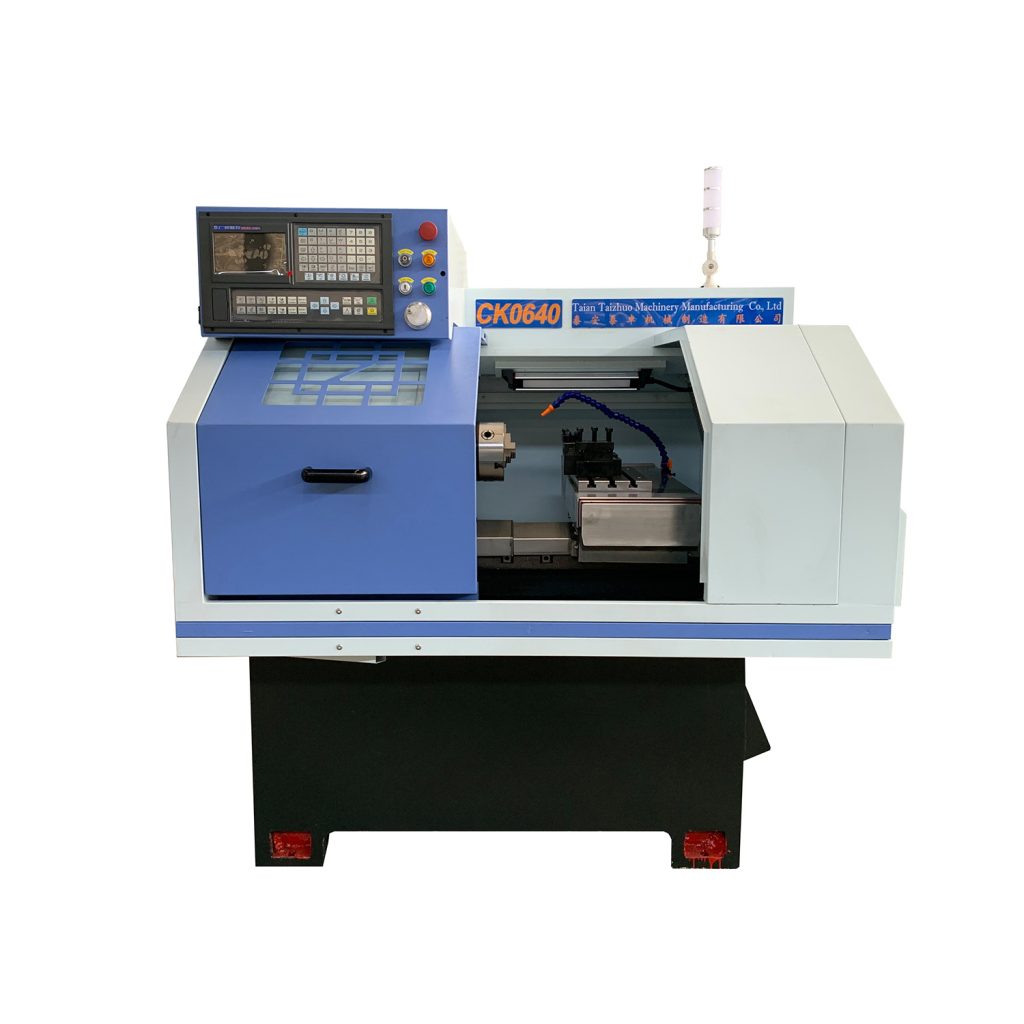
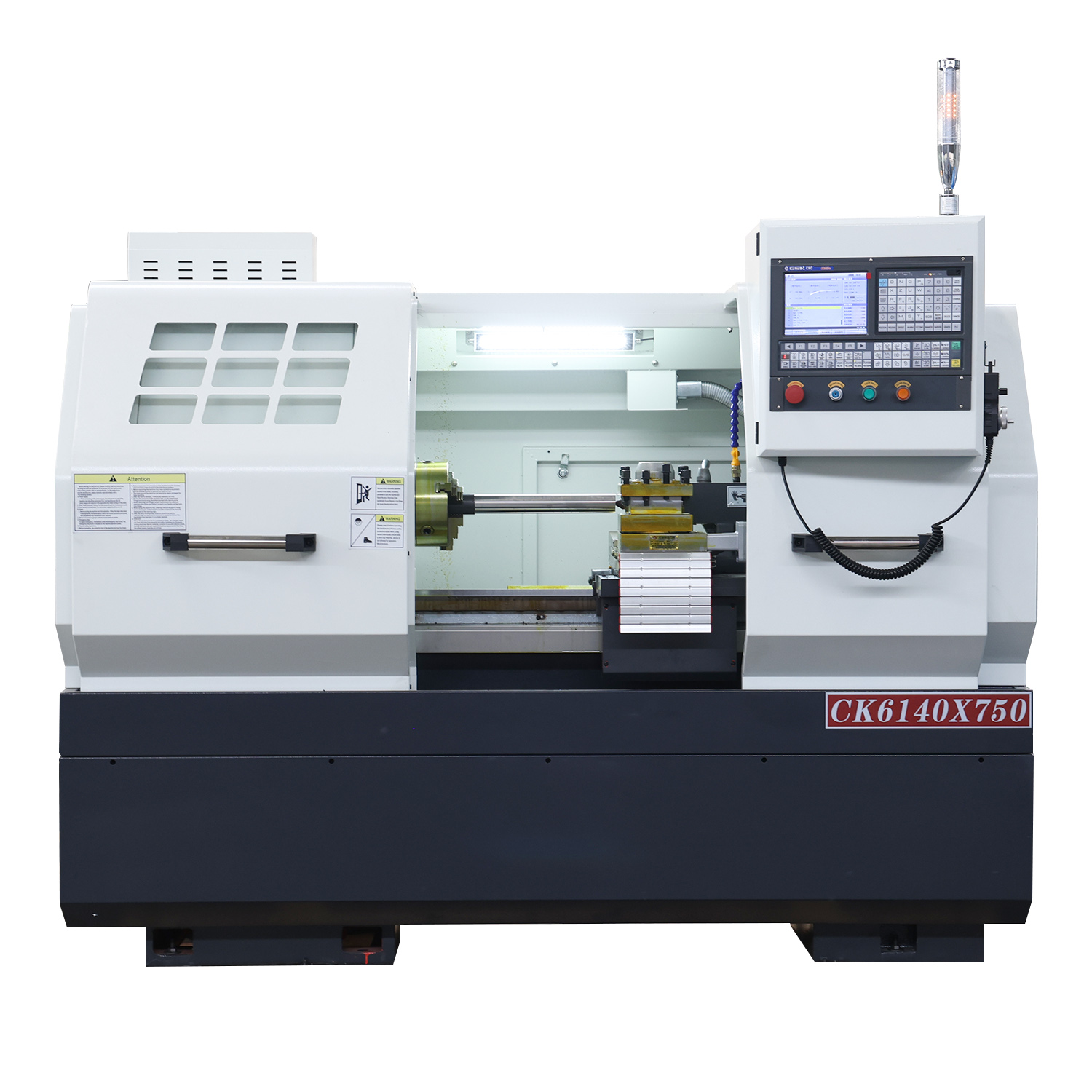
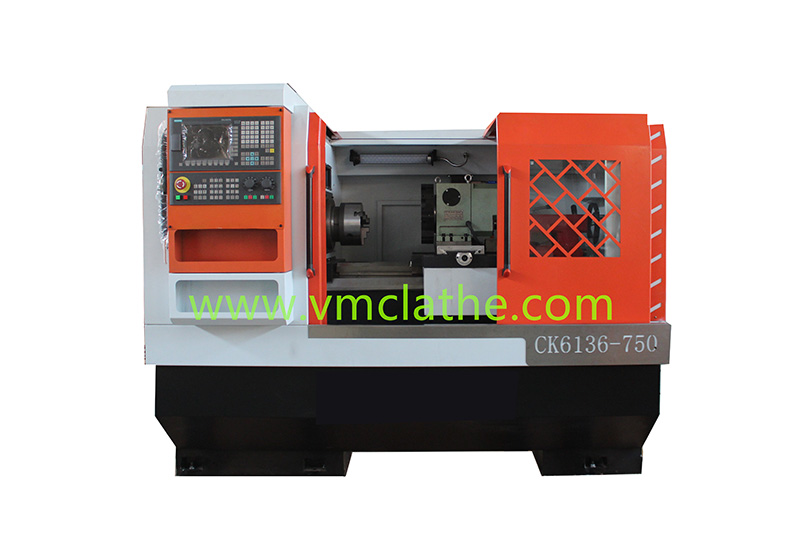
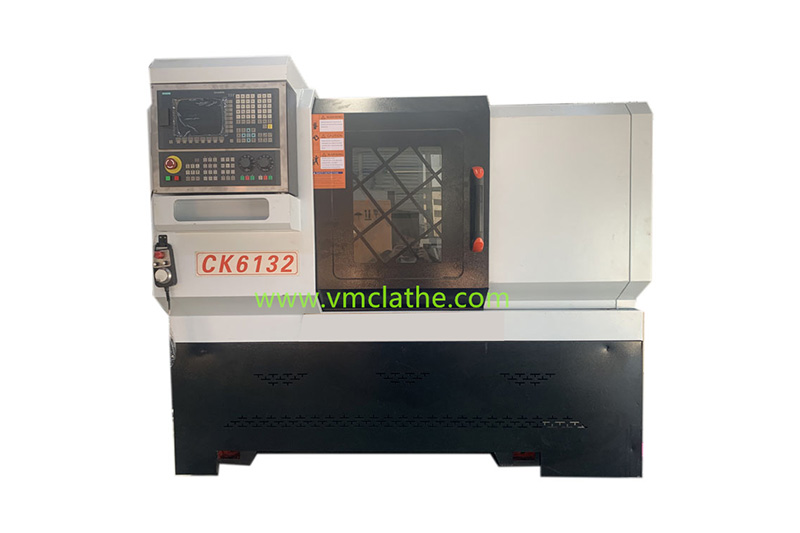
Flat-bed CNC lathes, with their advantages of high precision, high efficiency, and flexibility, combined with rational process design, can meet the machining needs of shaft parts. However, consideration should be given to the limitations of the machine’s rigid counterweight cutting and vibration control. The following is a detailed analysis of their use in shaft part processing:
1. Features of Flat-bed CNC Lathes
A. High Precision: Flat-bed CNC lathes utilize CNC systems for precise path planning and control, ensuring accurate part dimensions and shapes. When machining shaft parts, they ensure that the dimensional, shape, and positional accuracy meet design requirements.
B. High Efficiency: Flat-bed CNC lathes feature a high degree of automation, enabling multi-tasking and improving production efficiency. When machining shaft parts, they can reduce auxiliary time such as tool changes and tool setting, thereby improving machining efficiency.
C. Flexibility: Flat-bed CNC lathes can adapt to the machining needs of various shaft parts, including those with complex shapes, non-standard dimensions, and special requirements. By modifying the CNC program, machining parameters and paths can be quickly adjusted to achieve the machining of different parts.
2. Process Flow for Shaft Parts Machining on a Flat-Bed CNC Lathe
A. Pre-Machining Preparation:
a) Measure the part’s dimensions and analyze its shape to ensure that the machining accuracy meets the requirements.
b) Calibrate and debug the flat-bed CNC lathe to ensure stable operation.
c) Develop a machining process plan based on the part drawing and machining requirements, including the machining sequence, machining method, and machining parameters.
B. Rough Machining:
a) The purpose of rough machining is to remove material to prepare for subsequent finishing. On flat-bed CNC lathes, larger depths of cut and feed rates are typically used to improve machining efficiency.
b) During machining, closely monitor machining conditions, such as cutting force, temperature, and vibration, to ensure a smooth process.
C. Finishing:
a) The purpose of finishing is to improve the part’s dimensional accuracy and surface finish to meet design requirements. On a flat-bed CNC lathe, a smaller depth of cut and feed rate should be used to reduce machining errors.
b) During finishing, machining parameters such as cutting speed and cutting fluid usage must be strictly controlled to ensure machining quality.
c) After finishing, the part must be inspected to ensure that its size, shape, and surface quality meet the required specifications.
3. Considerations for Machining Shaft Parts on a Flat-Bed CNC Lathe
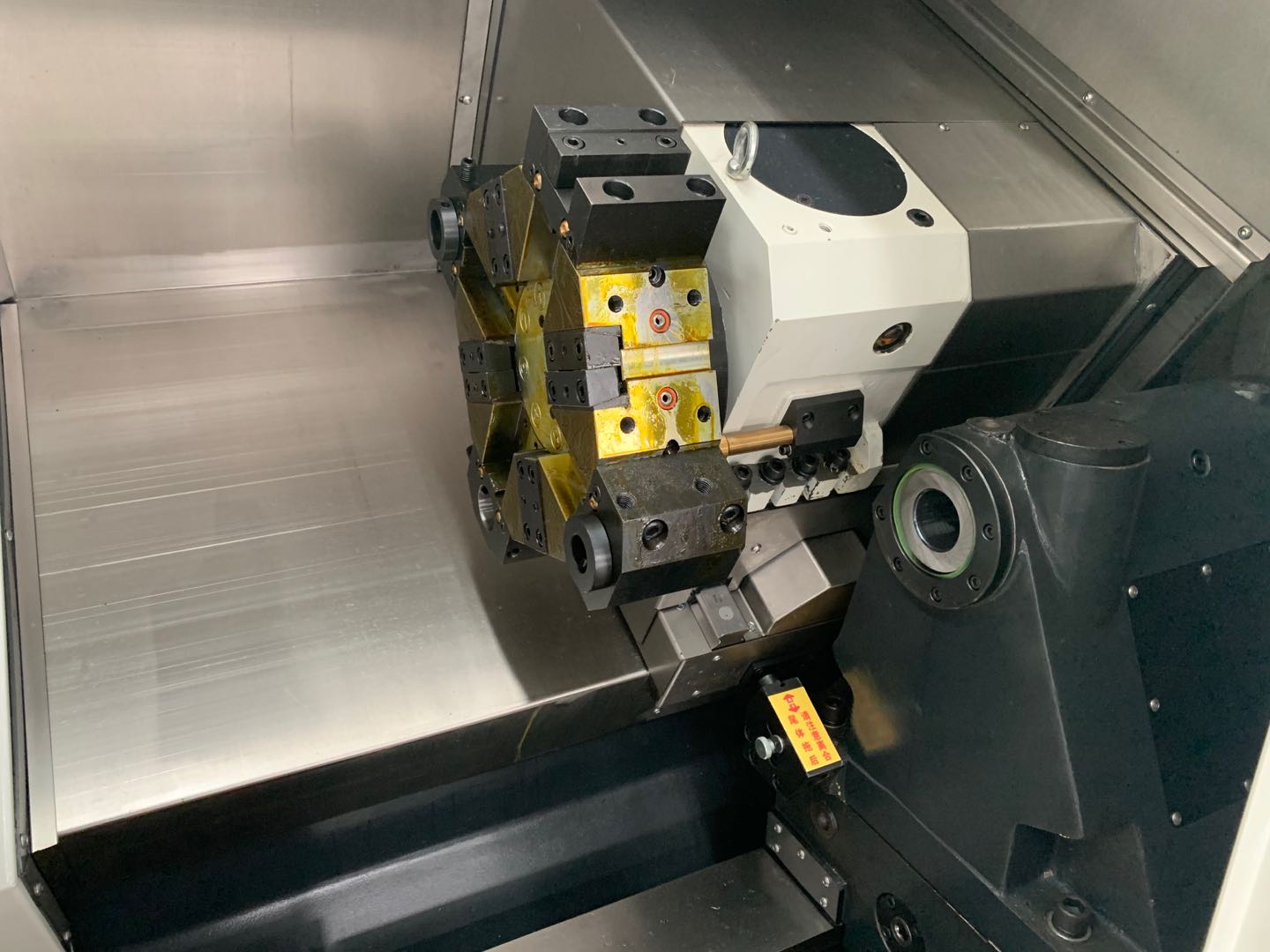
A. Tool Selection:
a) Tool selection directly impacts machining efficiency and quality. When machining shaft parts, appropriate tools should be selected based on the part’s material, shape, and machining requirements.
b) For example, for carbide materials, tools with good wear resistance should be selected; for parts with complex shapes, multi-edge tools should be selected to improve machining efficiency.
B. Cutting Parameter Optimization:
a) Cutting parameter selection has a significant impact on machining efficiency and quality. When machining shaft parts, cutting parameters such as cutting speed, feed rate, and depth of cut should be optimized based on the part’s material, tool, and machining requirements. b) By optimizing cutting parameters, machining efficiency can be improved, costs can be reduced, and machining quality can be guaranteed.
C. Workpiece Clamping:
a) The workpiece clamping method significantly impacts machining accuracy and efficiency. When machining shaft parts, the appropriate clamping method should be selected based on the part shape and machining requirements.
b) For example, for long shaft parts, a two-center clamping method can be used to improve machining rigidity; for short shaft parts, a chuck clamping method can be used to improve clamping efficiency.
D. Vibration Control:
a) When machining shaft parts, vibration is likely to occur due to their long length and poor rigidity. Vibration can affect machining accuracy and surface quality, so measures must be taken to control it.
b) For example, vibration can be reduced by optimizing cutting parameters, selecting appropriate tools, and clamping methods. Furthermore, vibration damping devices can be used to further minimize the impact of vibration on machining quality.