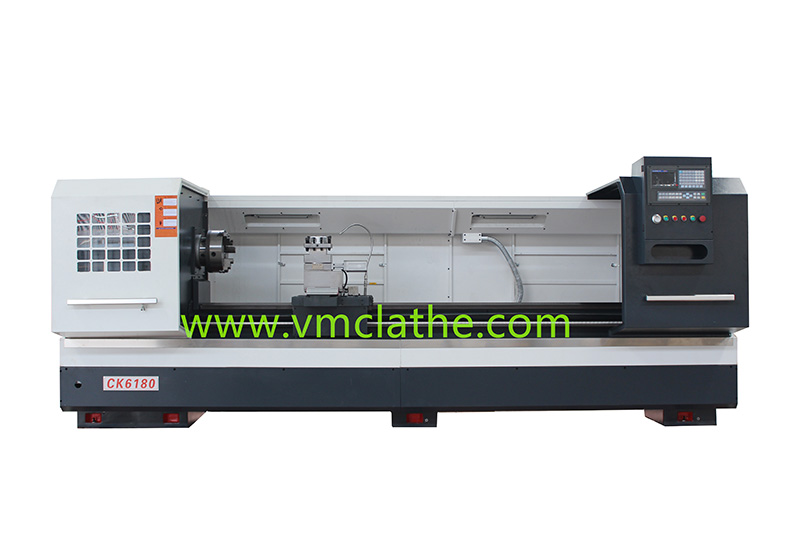
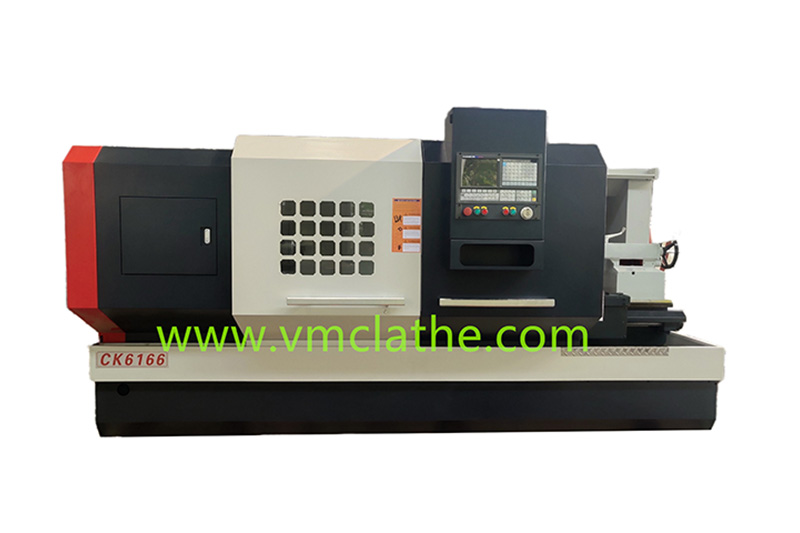
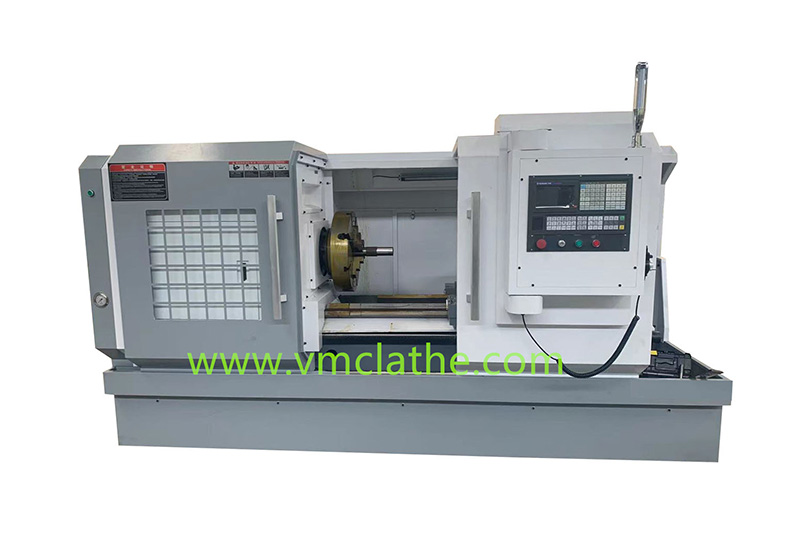
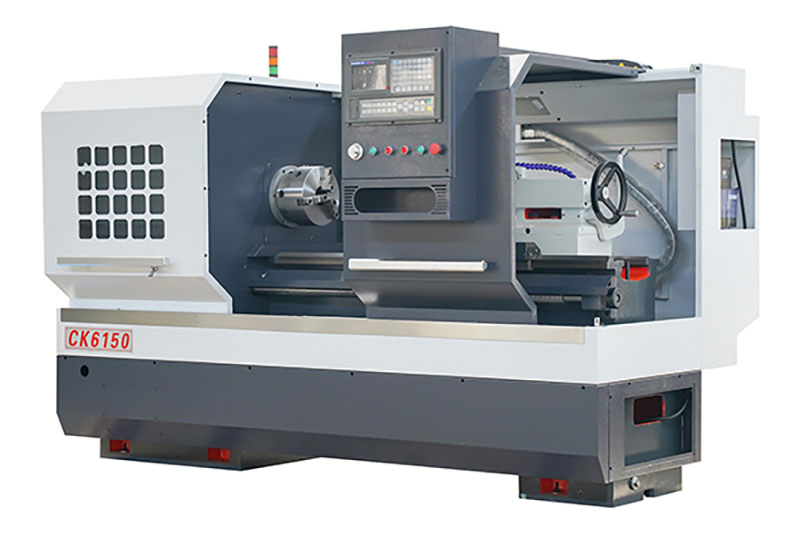
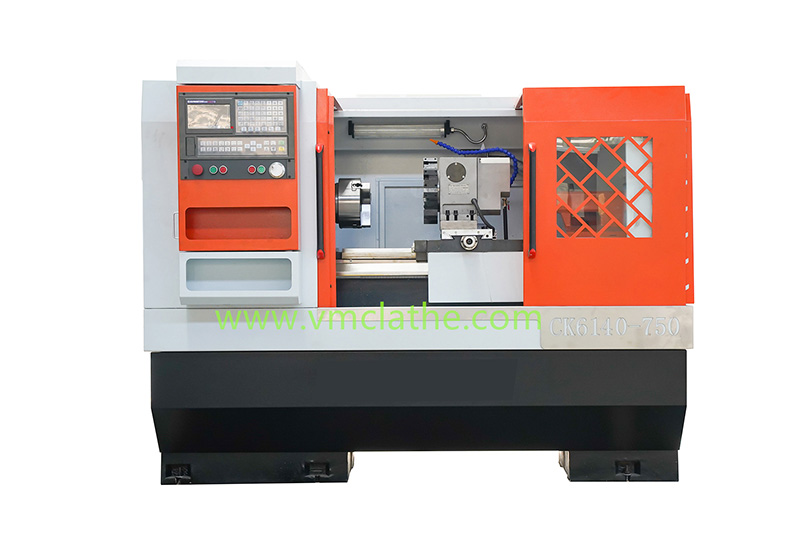
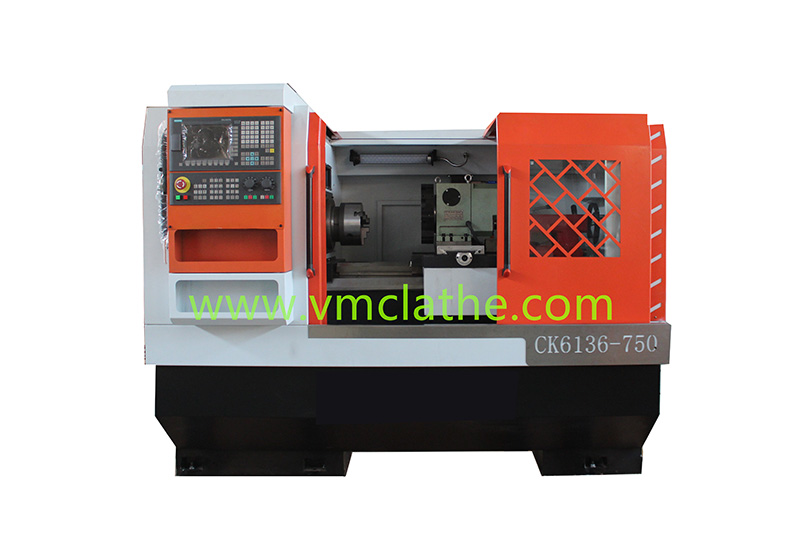
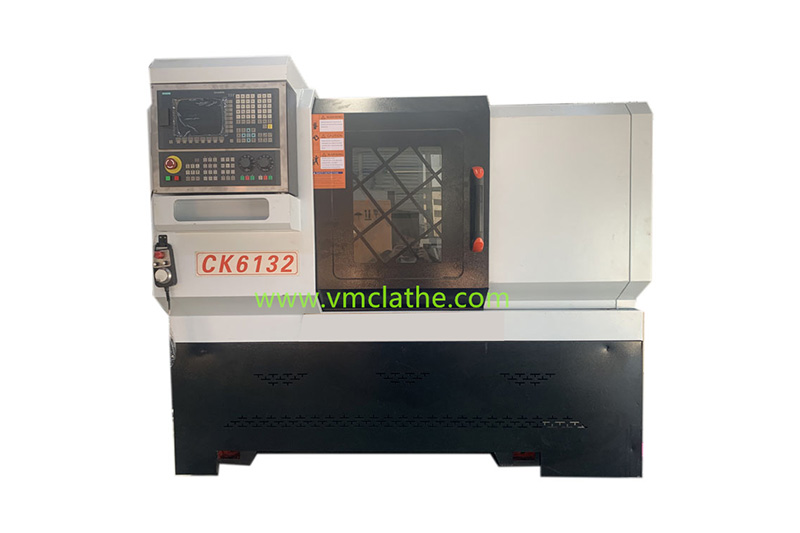
1. Determine the processing needs and precision requirements:
a) Processing accuracy: According to the precision requirements of the workpiece to be processed, select a CNC lathe with corresponding positioning accuracy and repeat positioning accuracy.
b) Surface roughness: Consider the surface roughness required for the workpiece to be processed and select a machine tool that can meet this requirement.
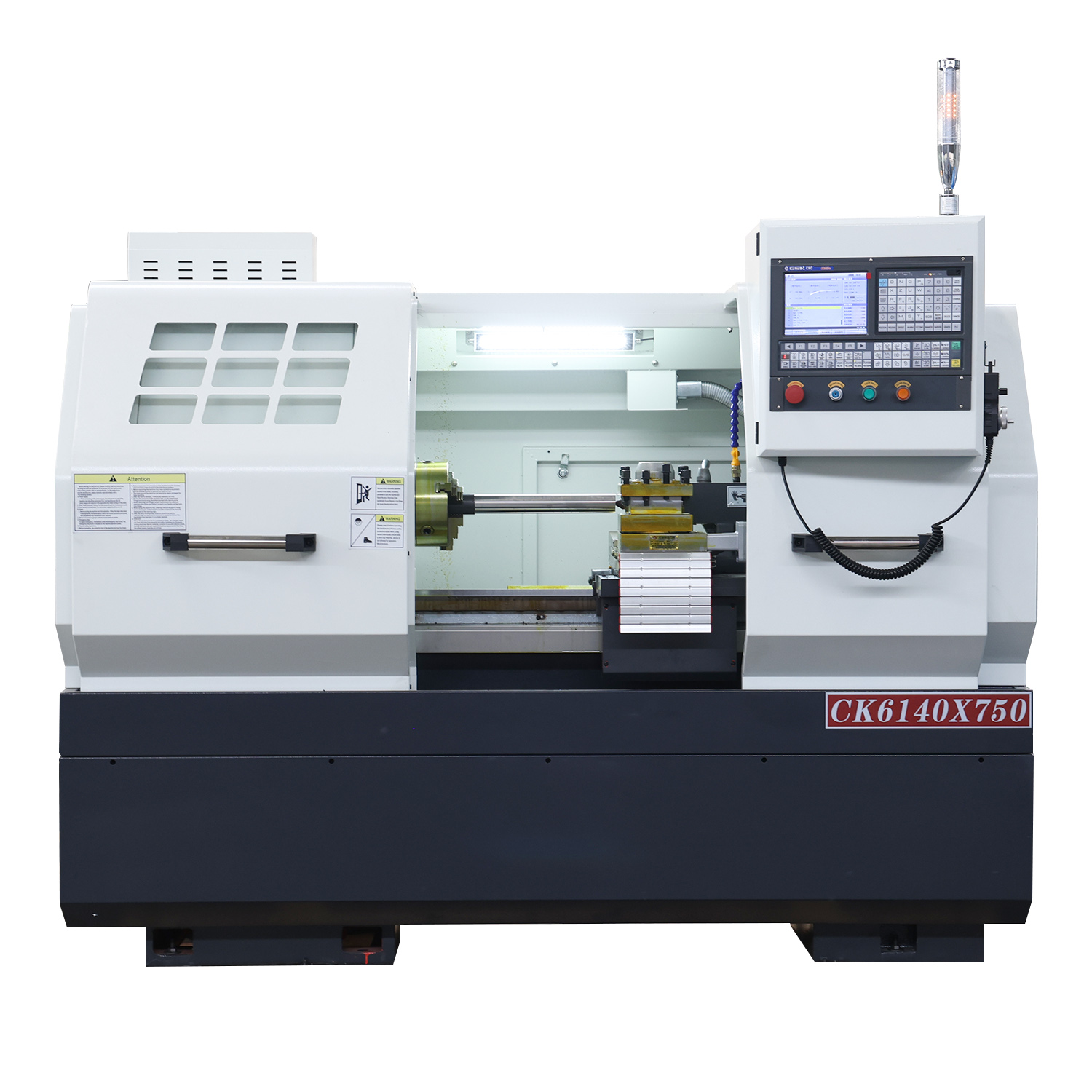
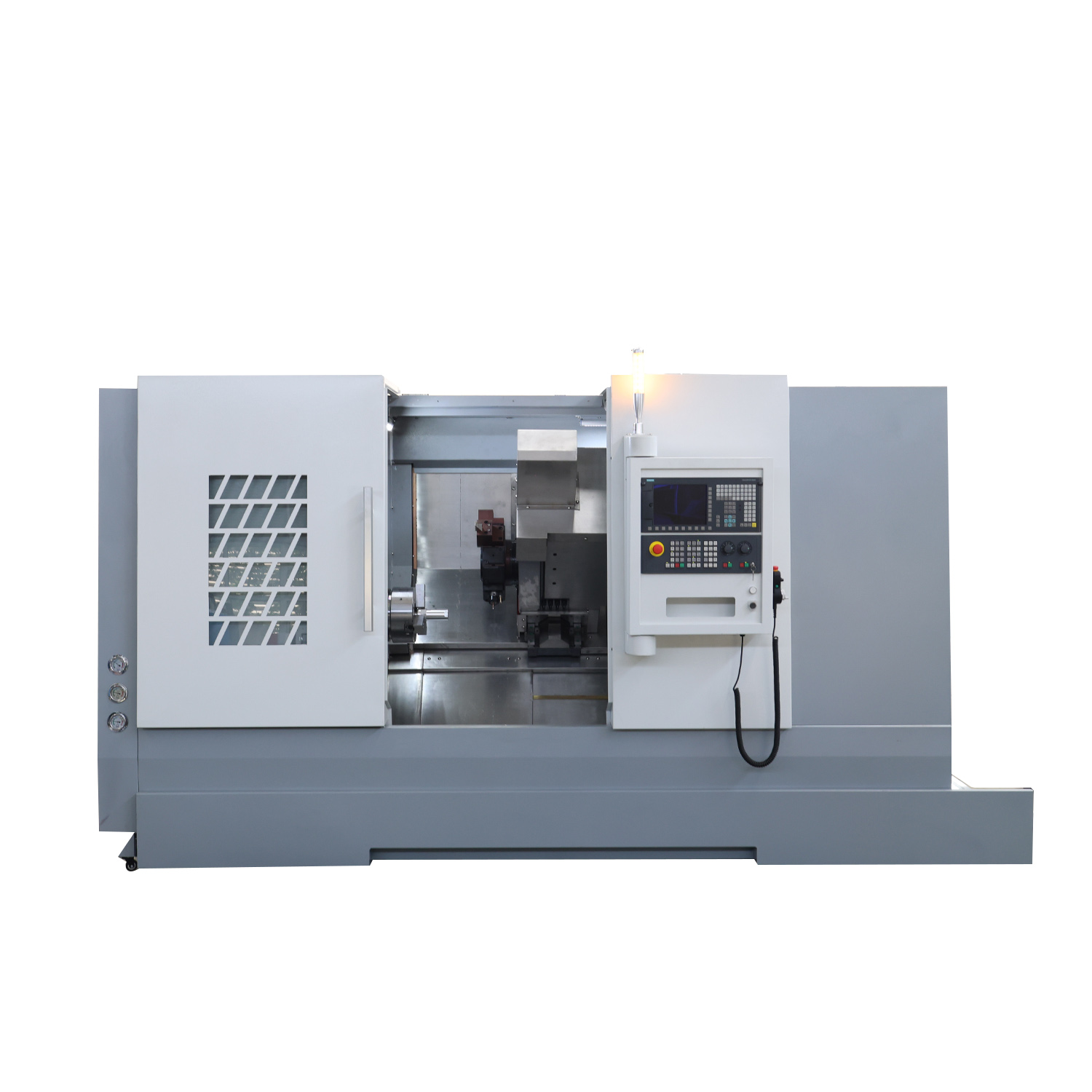
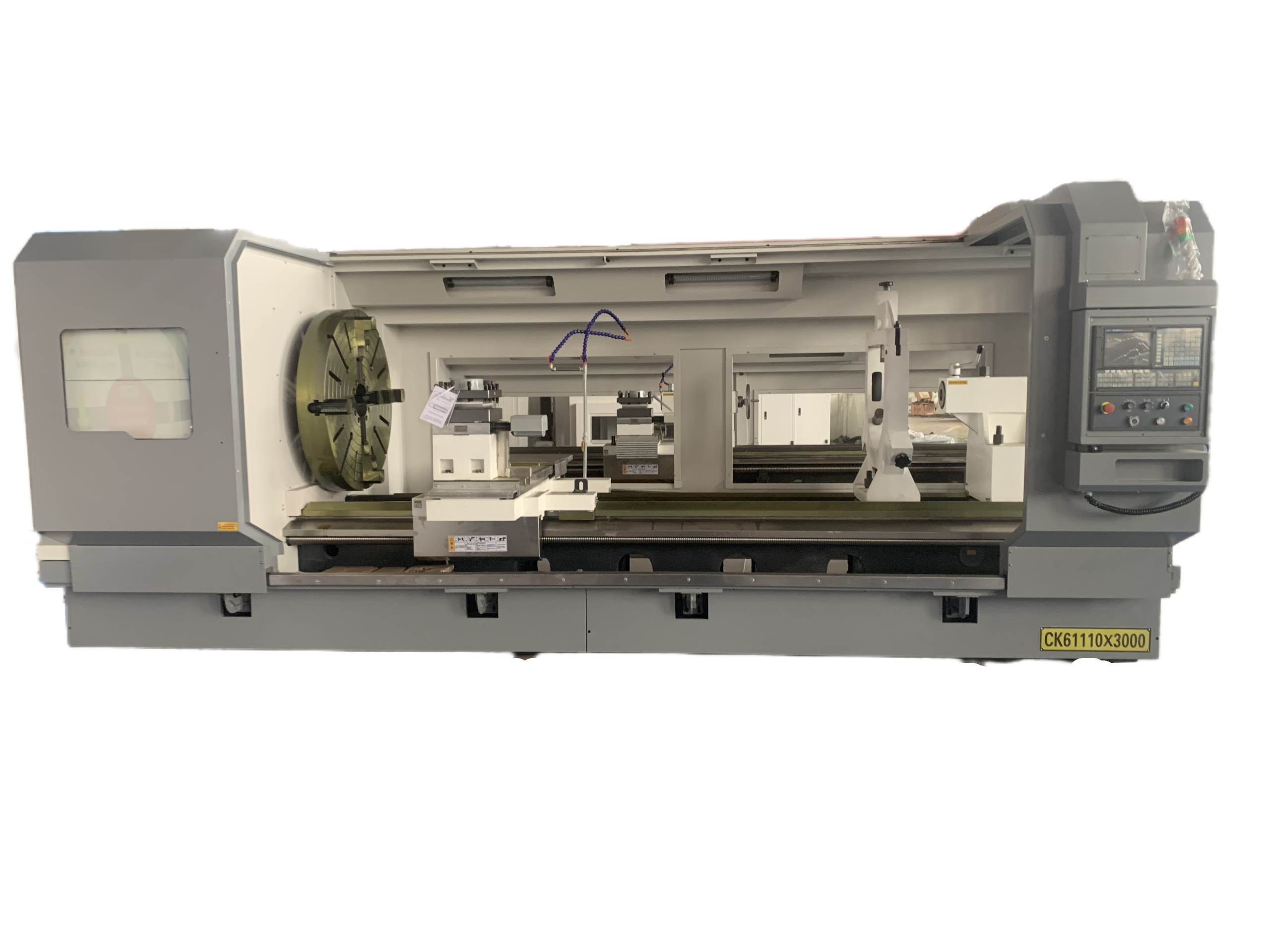
2. Evaluate the machine tool structure and rigidity:
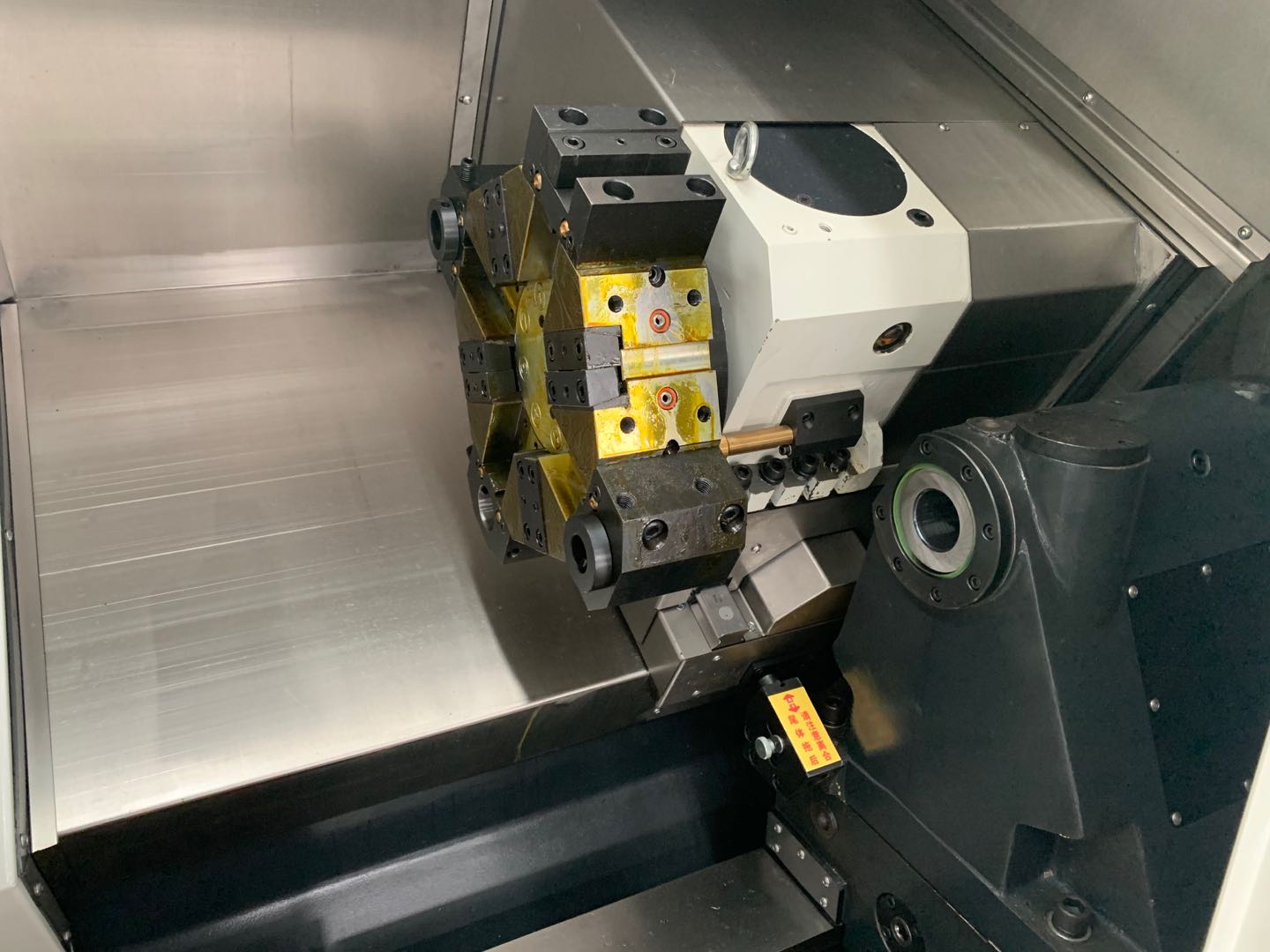
a) Bed design: Select a CNC lathe with a solid bed structure and good shockproof performance to ensure stability during the processing.
b) Guides and bearings: Pay attention to the accuracy grade, wear resistance and life of the guides and bearings, which directly affect the motion accuracy and service life of the machine tool.
3. Consider the control system and functions:
a) CNC system: Select a lathe with an advanced CNC system to achieve an efficient and accurate processing process. At the same time, consider the reliability and stability of the CNC system.
b) Functional module: Select a lathe with suitable functional modules according to the processing requirements, such as tool holder type, automatic feeding device, etc.
4. Understand after-sales service and technical support:
a) After-sales service: Choose a manufacturer that provides comprehensive after-sales service to ensure timely technical support and maintenance services during use.
b) Technical support: Consider whether the manufacturer provides training, technical consulting and other support services to help users better use and maintain the machine tool.
5. Comprehensively consider the cost-effectiveness:
a) Price factor: Under the premise of meeting the processing needs, choose a CNC lathe with a reasonable price.
b) Long-term benefits: Consider factors such as the service life and maintenance cost of the machine tool to evaluate its long-term benefits.